Nosophodipeptide, the chemical name is n-caproate-tyrosine-isoleucine – (6) aminocaproic acid amide, also known as Dihexa. It is a neuropeptide substance that has the function of regulating brain cell receptors and is mainly used as a neuroprotective agent and a promoter of memory enhancement. It is believed to improve the survival and function of nerve cells and effectively promote the generation of neural connections, thereby improving cognitive ability and memory.
Nogudipeptide is an orally active substance that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. It is an analogue extracted from angiotensin 4 and has a high binding affinity to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor c-Met.
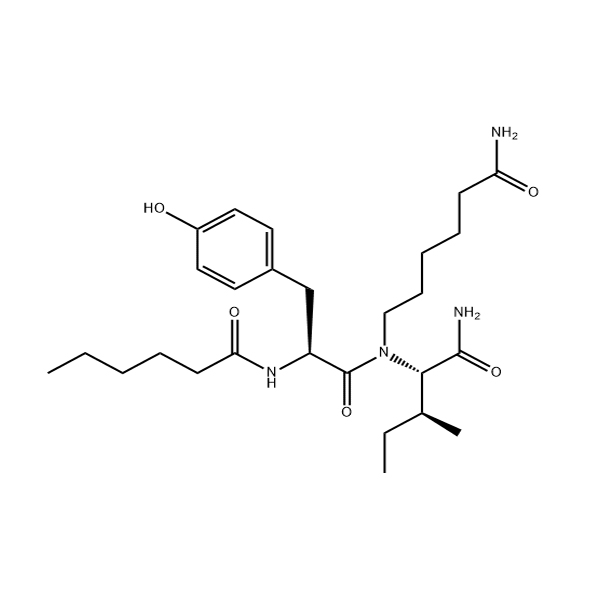
Nocidipeptide, a small peptide developed by a team at Washington State University, is seven times more potent than brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and is designed to improve specific cognitive functions, enhance psychological resilience, and improve short-term and long-term memory.
The synthesis of Nostrils dipeptides can be carried out by chemical synthesis, which involves a series of organic synthesis steps, including the reaction and purification of raw materials. In terms of safety, it has not been adequately studied, so its potential risks and side effects remain unclear. It is recommended to consult a physician or professional before using Dihexa. The correct method and dosage of use are very important, and excessive use may cause adverse reactions and health problems.
Post time: Apr-16-2025
