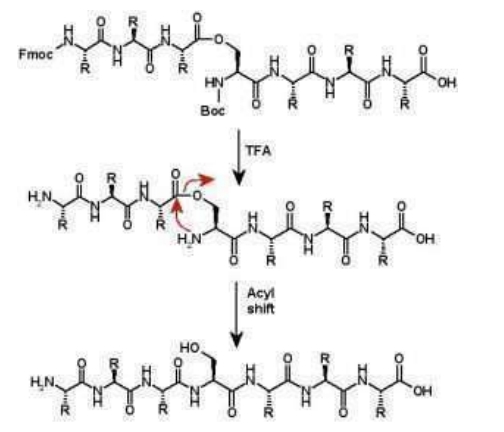
Isoacyl dipeptides are used to prepare peptide peptides in which the peptide chain is attached to a side chain oxygen atom of a serine or threonine residue instead of alpha nitrogen. Depsipeptides are less susceptible to aggregation than their standard peptide analogues because their structure disrupts the interchain hydrogen bonds responsible for aggregation. Isoacyl dipeptides are used to prepare dopaconate peptides in which the peptide chain is attached to a side-chain oxygen atom of a serine or threonine residue instead of an α-nitrogen atom. Depsipeptides are less susceptible to aggregation than their standard peptide analogues because their structure disrupts the interchain hydrogen bonds responsible for aggregation. This also improved the solubility of the depsipeptide compared to the standard analogue. The depsipeptide is stable at acidic conditions and can be purified by HPLC. When the pH is adjusted to 7.4 or higher, the peptide undergoes an O->N acyl transition to form the native peptide. Since HPLC purification of peptides is usually performed under acidic conditions, this provides an effective way to avoid solubility problems when purifying difficult peptides.
Isoacyl dipeptides can be formed on solid-phase resins, but acylated amino acids undergo racemization. However, when the reaction was carried out in solution, the degree of racemization was negligible. Therefore, the preformed isoacyl dipeptide was used to incorporate the O-acyl unit.
Isoacyl dipeptides are useful building blocks for the assembly of large peptides and small proteins by fragment condensation. In addition to improving the solubility of peptide fragments, isoacyl dipeptides have other benefits. Unlike conventional peptides, peptides containing isoacyl-dipeptides at the C terminus can be coupled to other peptide fragments, while the C-terminal amino acids are almost devoid of racemization. By designing peptide fragments with isoacyl dipeptides at the C terminus, large peptides or small proteins can be efficiently prepared with high diastereomeric purity.
Techniques for the use of isoacyl dipeptides
They are most effective when isoacyl dipeptides are used at the initiation of the hydrophobic fragment of the peptide. In addition, isoacyl dipeptides are most effective when there are at least six amino acid residues between them and other aggregation destroying units, for example proline residues, pseudoproline, and amino acids with Hmb or Dmb protection. The isoacyl dipeptide should also be at least six amino acid residues from the C terminus.
Isoacyl dipeptides have been used to synthesize human insulin.
Post time: Apr-25-2024