According to the connecting way of amino acid and sugar, sugar peptide can be divided into four categories: O glycosylation, C a N glycosylation, dew saccharification and GPI (glycophosphatidlyinositol) connection.
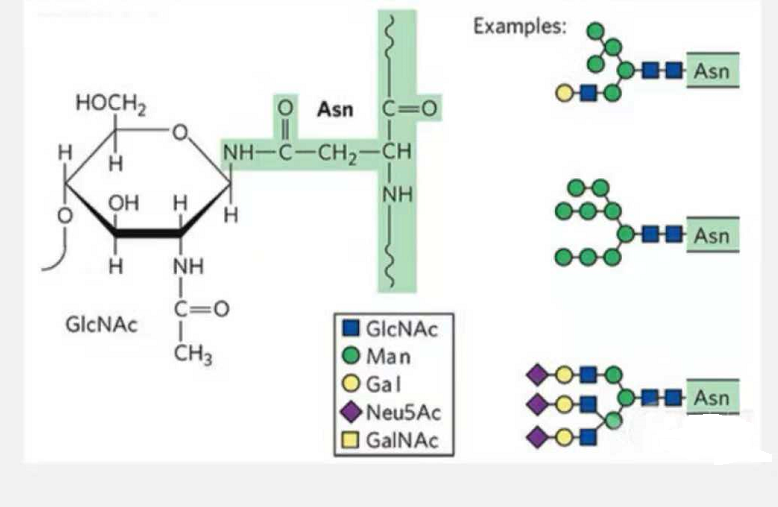
1. N-glycosylation glycopeptides are composed of N-acetamide glucose at the reducing end of the glycan chain (Glc-Nac) linked to the N atom on the amide group of the side chain of some Asn in the peptide chain, and the Asn capable of linking the glycan chain must be located in the AsN-X-Ser /Thr (X! =P) in the motif formed by the residues. The sugar is N-acetylglucosamine.
N-glycosylation modified structural glycopeptide
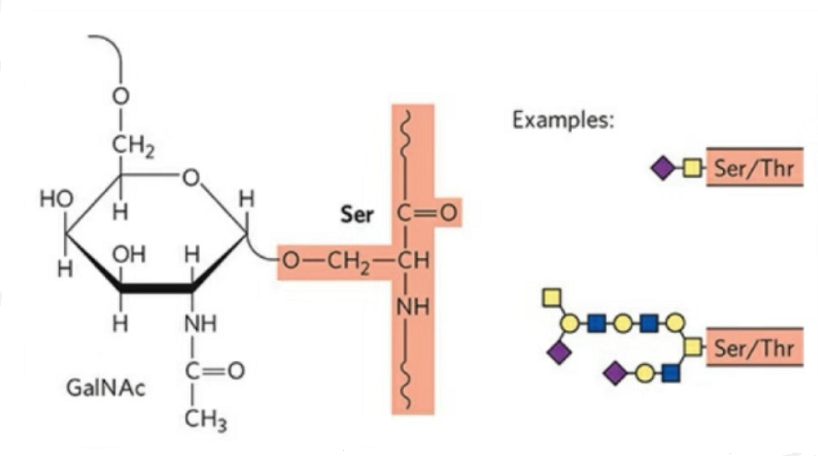
2. The structure of O-glycosylation is simpler than N-glycosylation. This glycopeptide is generally shorter than the glycan, but has more types than N-glycosylation. Ser and Thr can generally be glycosylated in the peptide chain. In addition, there are glycopeptides decorated with tyrosine, hydroxyl, and hydroxyproline glycosylation. The link position is the hydroxyl oxygen atom on the side chain of the residue. The linked sugars are galactose or N-acetylgalactosamine (Gal&GalNAc) or glucose/glucosamine (Glc/GlcNAc), mannose/mannosamine (Man/ManNAc), etc.
O-glycosylation modifies the structure
3. Glycopeptide O-GlcNAC glycosylation ((N-acetylcysteine (NAC)) (glcnAcN-acetylglucosamine/acetylglucosamine)
A single N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) glycosylation connects proteins O-GlcNAc to the hydroxyl oxygen atom of the serine or threonine residue of a protein. O-GlcNA glycosylation is O-GlcNAc monosaccharide ornament without glycan extension; Like peptide phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc glycosylation of glycopeptides is also a dynamic protein decoration process. Abnormal O-GlcNAc decoration can cause a variety of diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, tumors, Alzheimer’s disease and so on.
Glycosylation points of glycopeptides
The basic structures of polypeptide and sugar chains are linked to protein chains by covalent bonds, and the sites linking the sugar chains are called glycosylation sites. Since there is no template to follow the biosynthesis of glycopeptide sugar chains, different sugar chains will be attached to the same glycosylation site, leading to the so-called microscopic inhomogeneity.
Glycosylation of glycopeptides
1. Effect of glycopeptide glycosylation on therapy-efficacy of therapeutic proteins
In the case of therapy-therapeutic proteins, glycosylation also affects the half-life and targeting of protein drugs in vivo
2. Soluble glycopeptide glycosylation and proteins
Studies have shown that sugar chains on the surface of proteins can improve the molecular solubility of proteins
3. Glycopeptide glycosylation and protein immunogenicity
On the one hand, sugar chains on the surface of proteins can induce specific immune responses. On the other hand, sugar chains can cover certain surfaces on the protein surface and reduce its immunogenicity
4. Glycopeptide glycosylation that increases protein stability
Glycosylation can increase the stability of proteins to various denaturation conditions (such as denaturants, heat, etc.) and avoid the aggregation of proteins. At the same time, the sugar chains on the surface of proteins can also cover some proteolytic degradation points of protein molecules, thereby increasing the resistance of proteins to proteinases
5. Glycopeptide glycosylation that affects the biological activity of protein molecules
Changing protein glycosylation can also enable protein molecules to form new biological activities
Post time: Aug-03-2023