Helicobacter pylori, or Hp, is a risk factor for gastric cancer with a high prevalence. It is the only bacteria that can survive in the stomach at present and can adapt well to strong acidic environment. About 56% of the population in our country is infected.
In recent years, the high resistance of Hp to first-line antibiotics has become the major obstacle to eradication therapy in clinical medicine. In this regard, we have implemented the following solutions:
1. Bismuth quadruple therapy
Bismuth combined with antibiotics as a quadruple therapy has been recognized as a feasible method to eradicate Hp, especially for antibiotic resistant strains. Scientific studies have shown that bismuth quadruple therapy is more feasible than 14-day triple therapy in terms of efficacy and safety due to the increased resistance rate of Hp to clarithromycin.
2, diagnosis and treatment of Vonoprazan
Vonoprazan, a new potassiumcompetitive acid blocker, has been used to eradicate Hp. Vonoprazan, as a novel and highly potent antacid agent, does not require pharmacological activation, has a longer half-life, has a strong and sustained inhibitory effect on gastric acid secretion, and creates a neutral environment in the stomach that is not suitable for Hp survival.
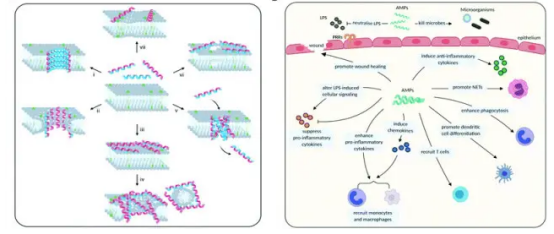
Antimicrobial peptides have a good inhibitory effect on Helicobacter pylori
3. Probiotics
Active and inactive peptides produced by probiotics can inhibit the growth and attachment of Hp. Moreover, probiotics could have beneficial effects on the side effects that may occur during the eradication of Hp infection, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and taste changes.
4. Vitamins
Vitamins (such as vitamin C and E) can reduce oxidation, eliminate reactive oxygen species, reduce nitrosamine components in gastric juice, play an antioxidant role, and play a protective role in the occurrence of gastric cancer.
5. Others
Studies reported that four anti-Hp compounds (apigenin, chrysin, kaempferol and hesperetin) had some bactericidal activity against Hp. A series of nitrobenzodiazole-based aflatoxin inhibitors have been developed. They have low toxicity and are effective against Hp strains resistant to metronidazole, clarithromycin and rifampicin.
Antimicrobial peptides can be precisely applied to anionic bacterial membranes to increase membrane permeability and cause cell death. Although the exploration of anti-biofilm is still in its initial stage, two synthetic anti-biofilm peptides (IDR-1018 and DJK-5) have been found to have inhibitory effects on Hp biofilms.
At the level of vaccine research, it is known that the oral vaccine based on Saccharomyces cerevisiae can effectively reduce the bacterial load after Hp infection.
Post time: Jan-23-2024