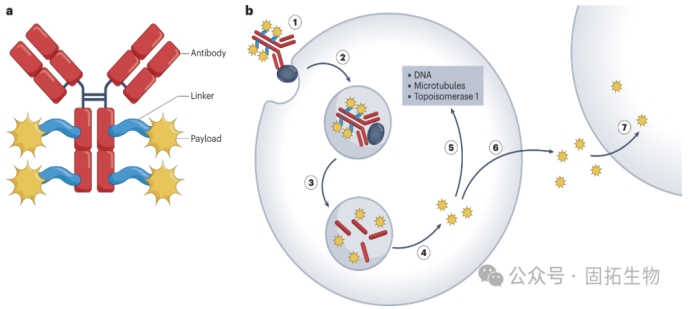
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is a targeted cancer therapy that combines the specificity of a monoclonal antibody with the cytotoxicity of a drug. Peptide adapters play a crucial role in ADC design because they link antibody and cytotoxic payloads, facilitating the control and release of drugs in target cells. The choice of connector can affect the stability of the ADC, the kinetics of drug release, and the overall effect. The choice of the specific connector depends on the pharmacokinetics of the ADC, the desired release mechanism, and the characteristics of the drug payload. It is important to balance circulatory stability with target-effective drug release to maximize the therapeutic effect of ADC. In addition, advances in connector technology continue to contribute to the development of novel and improved ADCs for cancer therapy.
Advantages of peptide connectors
1. Biocompatibility
The peptide adaptor is composed of natural amino acids, is biocompatible, and is unlikely to induce an immune response. This helps to improve the overall safety of the ADC.
2. Specificity and selectivity
The peptide adaptor can be designed to be a specific cut point for protease overexpression in target cells. This allows selective drug release in the tumor microenvironment, thereby enhancing the therapeutic window.
3. Stability of circulation
Peptide adapters can be designed to ensure their stability in the bloodstream, thereby minimizing premature drug release during circulation. This stability is essential to maintain the integrity of the ADC and prevent off-target effects.
4. Adjustable pharmacokinetics
It can fine-tune the properties of the peptide linker, such as its size and hydrophilicity, and thus affect the pharmacokinetics of the ADC. This tunability can optimize drug delivery and distribution in vivo.
5. Easy to synthesize
Peptide synthesis technology has matured, making the design and production of peptide connectors relatively simple. This ease of synthesis helps to improve the scalability and cost effectiveness of ADC fabrication.
6. pH sensitivity
Some peptide adapters can be designed to be pH sensitive, allowing drug release in the acidic environment of target cells or lysosomes. This pH response enhances the specificity of the drug for cancer cells.
7. Versatility
Peptide connectors can be designed for a variety of functions, such as promoting site-specific decoration, improving solubility, or improving overall stability. This versatility facilitates the design of ADCs with optimized properties.
8. Adequate characterization of the cleavage mechanism
Cellular proteases hydrolyze and cleave proteins of peptide adapters is an adequate biological process. This predictability contributes to a better understanding of drug release mechanisms and facilitates the rational design of ADCs.
Post time: Apr-10-2024
