gene cloning is the acquisition or generation of the target gene and a vector with independent replication ability to combine (vector) gene patchwork recombination, introduced into the recipient cells for asexual reproduction, and then produce new gene molecules.
Since the first DNA molecular cloning and recombination in the 1970s, gene cloning has become a key technology in biology, which has promoted the progress of biological molecular science and effectively promoted the rapid development of biomedical research and industry.
Objective
gene cloning technology can help to accurately analyze the expression and regulation of target genes, as well as the interaction of proteins, including regulatory elements, transcription factors and non-coding RNA. Second, it can be used for large-scale production of proteins that are difficult to obtain naturally. It can then be used to shape and engineer biological genome structures for greater applications. In addition, in recent years, with the increase in the demand for gene sequencing and analysis and the development of next-generation sequencing technology (NGS) gene cloning technology is also playing an increasingly important role in the development of gene cloning technology.
Classification of
According to the type of gene cloning, it can be divided into the following three categories:
1, classical gene cloning requires restriction enzymes and ligases. It is also the most widely used gene cloning method at present, which is easy to operate. However, it is generally suitable for small fragment gene cloning due to restriction of endonuclease restriction sites and ligase efficiency.
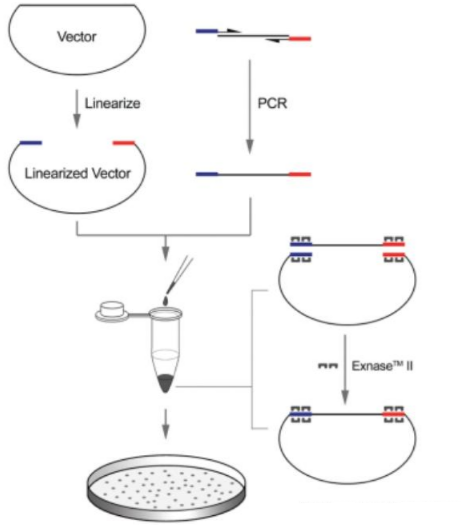
2. gene cloning that requires decorative enzymes does not require restriction enzymes and ligases, which improves the flexibility and application space of gene cloning such as UDG (uracil DNA glycosylase) cloning, and has the characteristics of simple operation and high cloning efficiency.
3. gene cloning that requires recombinases can not only achieve high-throughput cloning, but also be applied to multi-system expression vectors such as prokaryotes, yeast, insect cells and mammalian cells, using recombinases and specific recognition points to achieve efficient and efficient targeted cloning. At present, gene cloning technologies based on recombinant enzymes, such as GateWay technology and Golden Gate technology, have attracted wide attention.
Methods
The classical gene cloning methods mainly include: purposive gene preparation, restriction enzyme digestion and cleavage of the purposive gene and vector, the use of DNA ligase to cleave the gene and vector, and the preparation of DNA recombinant. Introduction of DNA recombinants into host cells, selective cloning and recognition, and expansion and expression of target genes in host cells.
Post time: Mar-29-2024
