The introduction and widespread use of angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and epinephrine P-receptor (P-receptor) blockers in the treatment of heart failure was a key turning point in pharmacotherapy for heart failure. However, the mortality rate of heart failure, especially advanced heart failure, is still very high. There are also very few new drugs that are effective in treating acute heart failure and have fewer side effects. Therefore, the continuous search and exploration of new effective drugs for the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure is still a key and difficult task faced by cardiovascular pharmacological staff and cardiovascular clinicians.
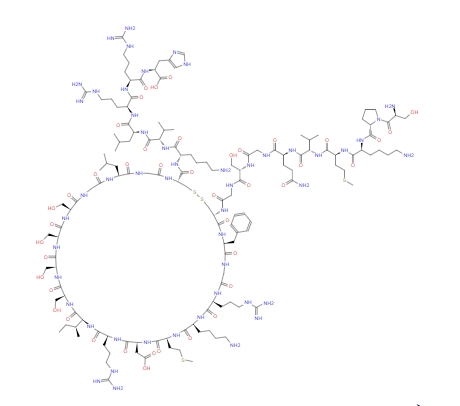
Nesiritide acetate is a synthetic human brain natriuretic peptide obtained from Escherichia coli using recombinant DNA technology, and its efficacy is very similar to that of human BNP. “It is a polypeptide of 32 amino acids linked by a disulfide bond between the l0 and 26 amino acids (both cysteine), forming a loop of l7 amino acids.” In recent years, many studies have proved that Nesiritide acetate has a definite therapeutic effect on the diagnosis and treatment of heart failure, especially acute heart failure.
Side effects
Side effects of Nesiritide acetate were few and not serious. Common side effects were chest pain, hypotension, nausea, abdominal pain, and headache. The study showed fewer side effects in the Nesiritide acetate group than in the nitroglycerin group.
Common Cautions
Blood pressure monitoring should be emphasized during medication. “Nesiritide acetate should not be taken for hypotension, valvular stenosis, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, restrictive cardiomyopathy, constrictive pericarditis, or pericardial tamponade.” Use with caution in pregnant and lactating women.
Post time: Apr-17-2024